
Diagnosing and Management of Canine Giardiasis
|
Several critical case management points to consider:>
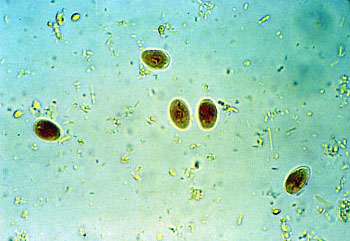
- Since the infectious cysts are shed in the feces in widely varying amounts, you cannot correlate the number of cysts found in testing to the severity of disease.
- 20% of positive animals do not shed cysts on any single day, therefore Zn sulfate w/ Lugol’s testing for three consecutive days is required to declare an animal negative.
- In Acute clinical animals, the Snap Test works well; Snap Test sensitivity of 95% is equal to the Zn sulfate w/ Lugol’s sensitivity at 95%.
- In Chronic carriers, the Snap Test sensitivity is only 50% compared to the Zn sulfate w/ Lugol’s at a sensitivity of 85%.
- Three days of a direct fecal smear examination only yields a 50% sensitivity.
- Fenbendazole (Panacur) is a better treatment than metronidazole.
- All treatment regimens should include bathing the animal’s perineal area as the live cysts found on the hair easily re-infect the animal and/or infect their housemate.
Preferred Centrifugation Method:
To begin: Mix 2-5 grams of fresh feces (about the size of a quarter) with 5-10 ml of floatation solution (zinc sulfate) in a beaker.
For this test, you will need to use zinc sulfate with a 1.18 specific gravity
-
Pour the mixture into a centrifuge tube after straining through a kitchen/tea strainer.
-
Next add floatation solution: fill the tube to within ~ 1 cm of the top.
-
Place the tube in your centrifuge, balance it, and spin for 5 minutes @ ~ 1300 rpm.
- You can use a swing or fixed head centrifuge with equal success. -
Remove the tube, place it in a rack, and slowly fill with your floatation solution to form a slight positive meniscus.
-
If you use a squirt bottle for this step, be careful to not cause turbulence in the centrifuged fluid, as this will drive the cysts that are floating deeper into the tube.
-
Cover the tube with a cover slip and let sit for 10 minutes.
- This allows the cysts to float the last 1 cm. -
Place one drop of Lugol's iodine on a microscope slide.
- Remove the cover slip, place it onto the iodine drop and examine for the brown-stained cysts.
SNAP Test:
-
Remove the test kit from the refrigerator and let it warm to room temperature.
- Pull off the tube that covers the conjugates swab device and coat the entire swab tip with a thin layer of fecal material. Replace the tube over the swab.
- Break the plastic valve stem inside the reagent bulb by bending the assembly back and forth at the neck.
- Hold the device swab tip down squeeze and release three to five times to pass the conjugates solution in the bulb to the swab tip.
-
Place the snap device on a flat surface. Using the swab bulb as a pipette, place 5 drops of the sample solution into the sample well of the snap device. Be careful not to splash the contents outside the sample well.
-
The sample will flow across the result window reaching the activation Circle in approximately 30 to 60 Seconds. When the sample first appears in the activation Circle, push the activator button firmly until it is flush with the device body. NOTE: If the sample does not flow to the activation Circle within 60 Seconds press the activator button after the sample has flowed across the result window.
- Wait eight minutes then read the test result.
Interpreting test results:
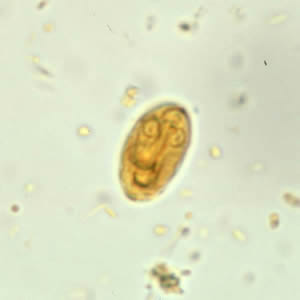
The test is positive if the color on the sample spot is darker than the color on the negative control spot.
The test is negative if the color on the sample spot is = to or < the color on the negative control spot.